Table of contents
This is the third part of Algorand Starter series. On Algorand, smart signatures are small programs that are submitted as part of a transaction and evaluated at submission time. These types of signatures have two basic usage: escrow-type of account or authority delegation. This blog will provide basic knowledge and some examples for demonstration.
Algorand Starter series:
- Part 1: Client side
- Part 2: Stateful contract (Smart contract)
- Part 3: Stateless contract (Smart signature)
- Part 4: Test scripts
Contract accounts

Each unique compiled smart signature program corresponds to a single Algorand address, output by goal clerk compile. To use a TEAL program as a contract account, just send Algos to its address to turn it into an account on Algorand with a balance:
- On funding perspective, this account looks no different from any other Algorand account and anyone can send it Algos or ASA to increase its balance.
- On spending perspective, the transaction is approved only if the logic is passed. To spend from a contract account, create a transaction that will evaluate to True against the TEAL logic, then add the compiled TEAL code as its logic signature. Note that anyone can create and submit spending transaction as long as they have the compiled TEAL contract to add as a logic signature.
Delegated approval
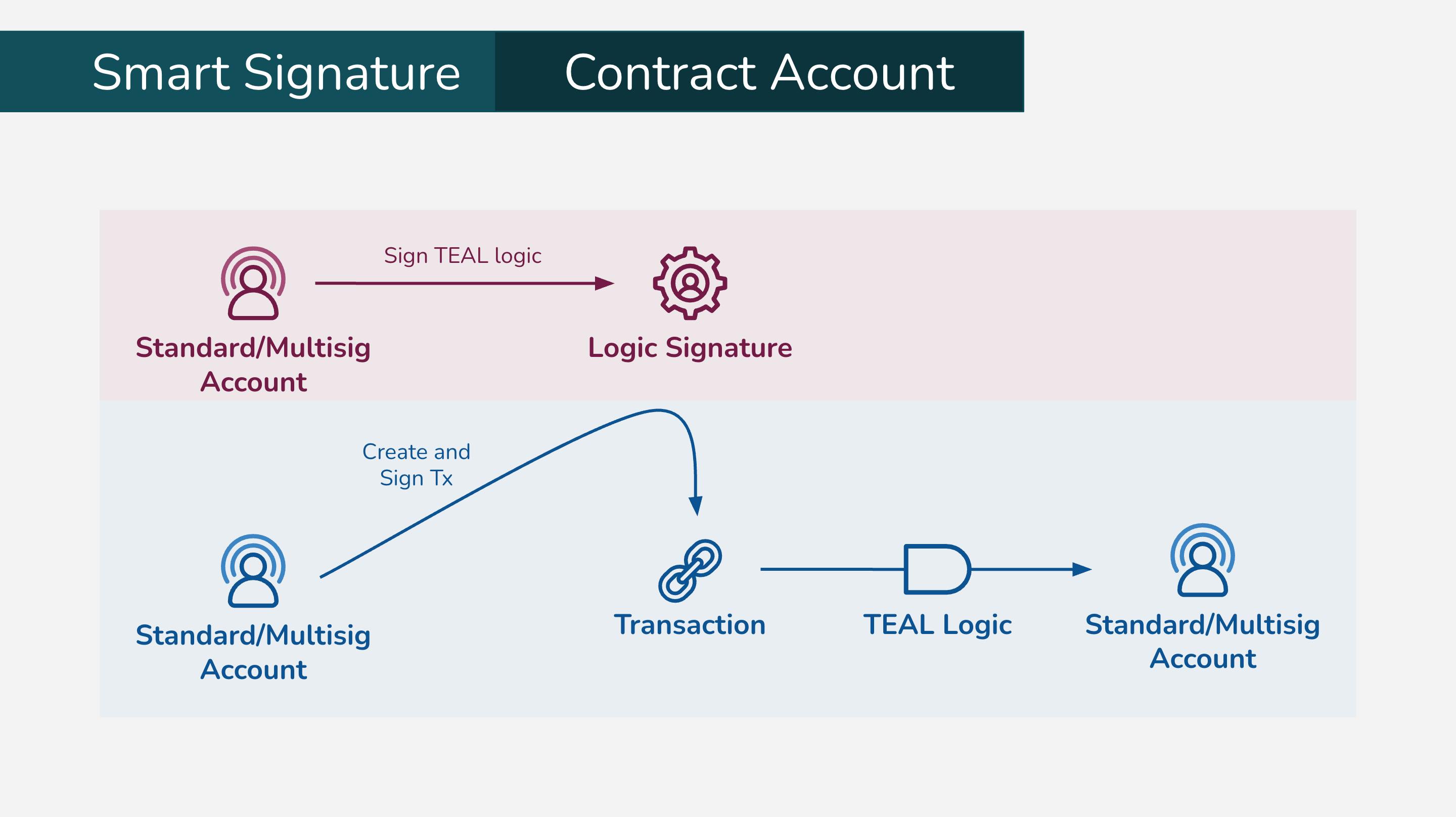
Smart signatures can also be used to delegate signature authority, which means that a private key can sign a TEAL program and the resulting output can be used as a signature in transactions on behalf of the account associated with the private key. The owner of the delegated account can share this logic signature, allowing anyone to spend funds from his or her account according to the logic within the TEAL program. For example, a mortgage company may provide logic to an account to remove a certain number of Algos from the account once a month. The user then signs this logic and once a month the mortgage company can submit a transaction from the signing account, but the transaction is signed by the smart signature and not the private key of the account. (Ref: Algorand Doc)
Examples
Let's get hand dirty with the contract account example below. It is a donation program, which anyone can send the fund to an address, and only a benefactor can claim the fund.
def donation_escrow(benefactor):
program = And(
Txn.type_enum() == TxnType.Payment,
Txn.receiver() == Addr(benefactor),
Global.group_size() == Int(1)
)
return compileTeal(program, Mode.Signature, version=5)
If people want to donate for someone, they just send to fund to the receiver directly. However, this example is just for quick study, we can add the vesting or other logics later. For now, donation_escrow is a very simple program. It will check if the transaction type is payment and the receiver is the targeted benefactor. Additionally, it guarantees that the transaction is not grouped with others. Next, we will compile this program to get a unique contract address.
from algosdk.v2client import algod
from pyteal import *
receiver_public_key = "UFAGBH5BHBAKDSSSBKP6LAZ7VFIA3ETNK7LVNEH6KXRRNTYE6WYHTEMEGU"
algod_address = "http://localhost:4001"
algod_token = "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa"
def compile_smart_signature(client, source_code):
compile_response = client.compile(source_code)
return compile_response['result'], compile_response['hash']
# ...
def main():
algod_client = algod.AlgodClient(algod_token, algod_address)
print("--------------------------------------------")
print("Compiling Donation Smart Signature ...")
stateless_program_teal = donation_escrow(receiver_public_key)
escrow_result, escrow_address = compile_smart_signature(algod_client, stateless_program_teal)
print("Program:", escrow_result)
print("Contract Address:", escrow_address)
main()
compile_smart_signature function will call to algod for compile program, and it will return the program bytecode with hash, which is contract address. We can compile many times, but the contract address is only 1 unique address.
$ python3 donation_smart_sig.py
--------------------------------------------
Compiling Donation Smart Signature ...
Program: BSABATEQIhIxB4AgoUBgn6E4QKHKUgqf5YM/qVANkm1X11aQ/lXjFs8E9bASEDIEIhIQQw==
Contract Address: UORLHSSLWN3DZVBLBG55MEU5A65CEH2QUXD4UCQWKMSLCSQOU5MBJGAIPQ
$ python3 donation_smart_sig.py
--------------------------------------------
Compiling Donation Smart Signature ...
Program: BSABATEQIhIxB4AgoUBgn6E4QKHKUgqf5YM/qVANkm1X11aQ/lXjFs8E9bASEDIEIhIQQw==
Contract Address: UORLHSSLWN3DZVBLBG55MEU5A65CEH2QUXD4UCQWKMSLCSQOU5MBJGAIPQ
We will send some ALGOs to the above contract address:
sender_mnemonic = "SENDER MNEMONIC"
def wait_for_confirmation(client, transaction_id, timeout):
start_round = client.status()["last-round"] + 1
current_round = start_round
while current_round < start_round + timeout:
try:
pending_txn = client.pending_transaction_info(transaction_id)
except Exception:
return
if pending_txn.get("confirmed-round", 0) > 0:
return pending_txn
elif pending_txn["pool-error"]:
raise Exception('pool error: {}'.format(pending_txn["pool-error"]))
client.status_after_block(current_round)
current_round += 1
raise Exception('pending tx not found in timeout rounds, timeout value = {}'.format(timeout))
def payment_transaction(creator_mnemonic, amt, rcv, algod_client)->dict:
params = algod_client.suggested_params()
add = mnemonic.to_public_key(creator_mnemonic)
key = mnemonic.to_private_key(creator_mnemonic)
unsigned_txn = transaction.PaymentTxn(add, params, rcv, amt)
signed = unsigned_txn.sign(key)
txid = algod_client.send_transaction(signed)
pmtx = wait_for_confirmation(algod_client, txid, 5)
return pmtx
def main():
# ...
print("--------------------------------------------")
print("Sending Fund to Donation Smart Signature ...")
amt = 2001000
payment_transaction(sender_mnemonic, amt, escrow_address, algod_client)
Attention again, mnemonic here is only for studying purpose, do not use in production code, use wallet instead. payment_transaction is just normal payment transaction: get suggested param, create Tx with sender and receiver, sign Tx, submit Tx, then wait for confirmation. Finally, we will withdraw fund from contract address to benefactor.
def lsig_payment_txn(escrowProg, escrow_address, amt, rcv, algod_client):
params = algod_client.suggested_params()
unsigned_txn = transaction.PaymentTxn(escrow_address, params, rcv, amt)
encodedProg = escrowProg.encode()
program = base64.decodebytes(encodedProg)
lsig = transaction.LogicSig(program)
stxn = transaction.LogicSigTransaction(unsigned_txn, lsig)
tx_id = algod_client.send_transaction(stxn)
pmtx = wait_for_confirmation(algod_client, tx_id, 10)
return pmtx
def main:
# ...
print("--------------------------------------------")
print("Withdraw from Donation Smart Signature ...")
withdrawal_amt = 80000
lsig_payment_txn(escrow_result, escrow_address, withdrawal_amt, receiver_public_key, algod_client)
Basically, lsig_payment_txn is just a normal payment transaction. The difference is only using logic signature, which is created from donation program with transaction.LogicSig, to sign the Tx. Finally, we can check the balance of contract address and benefactor at Algorand testnet explorer:
- Contract balance: testnet.algoexplorer.io/address/UORLHSSLWN3..
- Benefactor balance: testnet.algoexplorer.io/address/UFAGBH5BHBA..
Full code: github.com/liamhieuvu/algorand-first-contra..
Reference: developer.algorand.org/docs
Thank you for reading my blog

